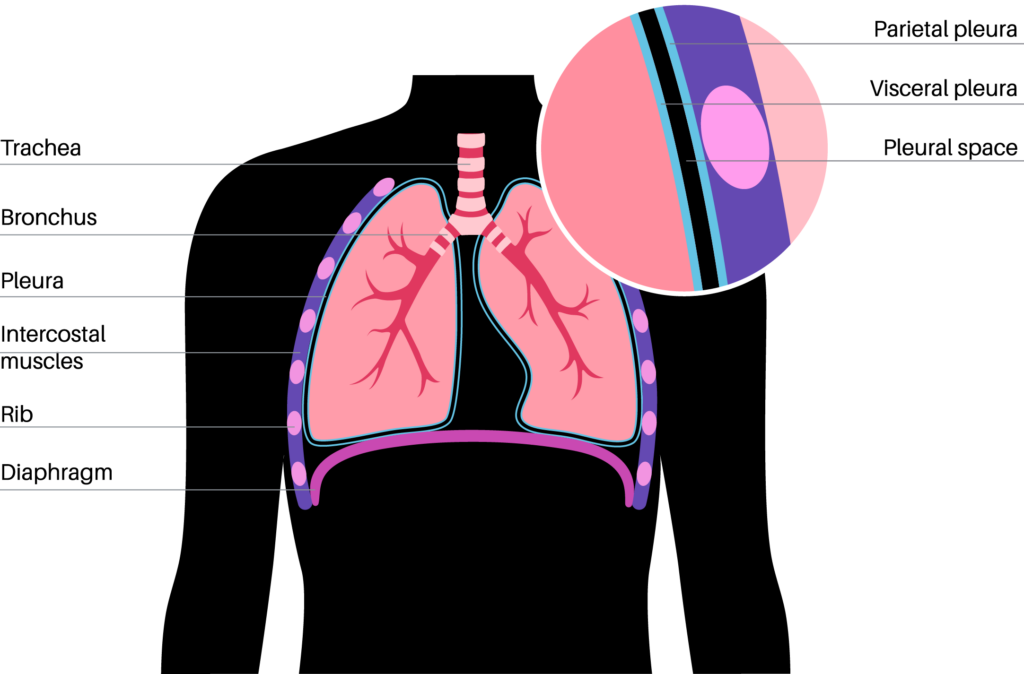
Mesothelioma is a cancer of the mesothelial lining that surrounds organs such as the lung, abdomen, heart, and testes. Most frequently, mesothelioma affects the lining of the lung, which is called the pleura, in which case it is called pleural mesothelioma. The second most frequent occurrence of mesothelioma is along the lining of the abdomen and, in that instance, it is called peritoneal mesothelioma. Occasionally, when pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma are both present, the disease is said to be dual compartment.
The two least frequent occurrences of this cancer are pericardial mesothelioma (along the lining of the heart), and tunica vaginalis (along the lining of the testes).
Symptoms
Symptoms of mesothelioma are not specific. Depending on the organs involved they are also generally very different one from the other. With pleural mesothelioma patients generally experience;
- a fluid buildup (pleural effusion),
- shortness of breath (dyspnea),
- cough, and
- fever.
Peritoneal mesothelioma patients tend to experience symptoms like:
- fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites),
- abdominal pain,
- increased abdominal girth,
- digestive issues, and an
- elevated white blood cell count.
Diagnosis
Survival
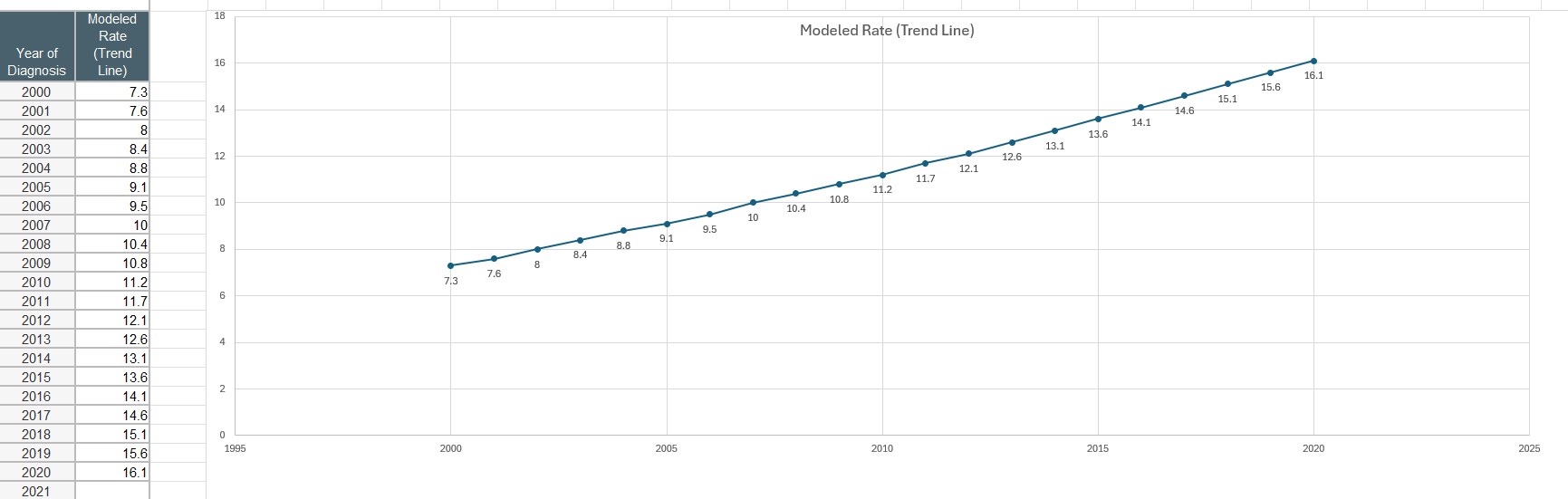
Based on a study from 2004, mesothelioma has a median survival of 12 months with treatment. In recent years, with the advent of immunotherapy, median survival has increased up to 18 months. Despite its poor prognosis, some patients do quite well with treatment, as evidenced by the recent increase in the 5-year survival rate. For best chances at longer survival, patients should be seen by a mesothelioma specialist.
Likely due to recent advances in treatment, the SEER database reports that in the last two decades mesothelioma survival doubled from 7.5% at 5 years in 2000 to well over 16% in 2020.